Northwest Villages Dentistry - Vesna Arezina DDS
Northwest Villages Dentistry - Vesna Arezina DDS
WELCOME TO Northwest Villages Dentistry
Vesna Arezina DDS
Welcome to Northwest Villages Dentistry - Vesna Arezina DDS, PA your local family dentist in Houston, TX, 77070. For over twenty years, Dr. Vesna Arezina has served her patients in Houston, TX. Our bilingual office is committed to providing complete, quality dental care in a pleasant and caring environment for the entire family.
Our Houston dentist offers a wide range of dental treatment options to make sure that all our patients receive the care that they need. Our office provides general and cosmetic dentistry (veneers, teeth whitening, white fillings, bonding, enamel shaping), family dentistry, and so much more. We prioritize serving patients seeking emergency dental care.
Northwest Villages Dentistry - Vesna Arezina DDS, PA is located near Jones Road, Grant Road, Tallow Wood, Willowbrook Mall, Cypress Creek High School, Bleyl Middle School, Hamilton Middle School, Cy-Creek High School, Norchester, Lakewood Forest, Cy-Fair, Tomball, Northwest Houston, and Klein area.

.
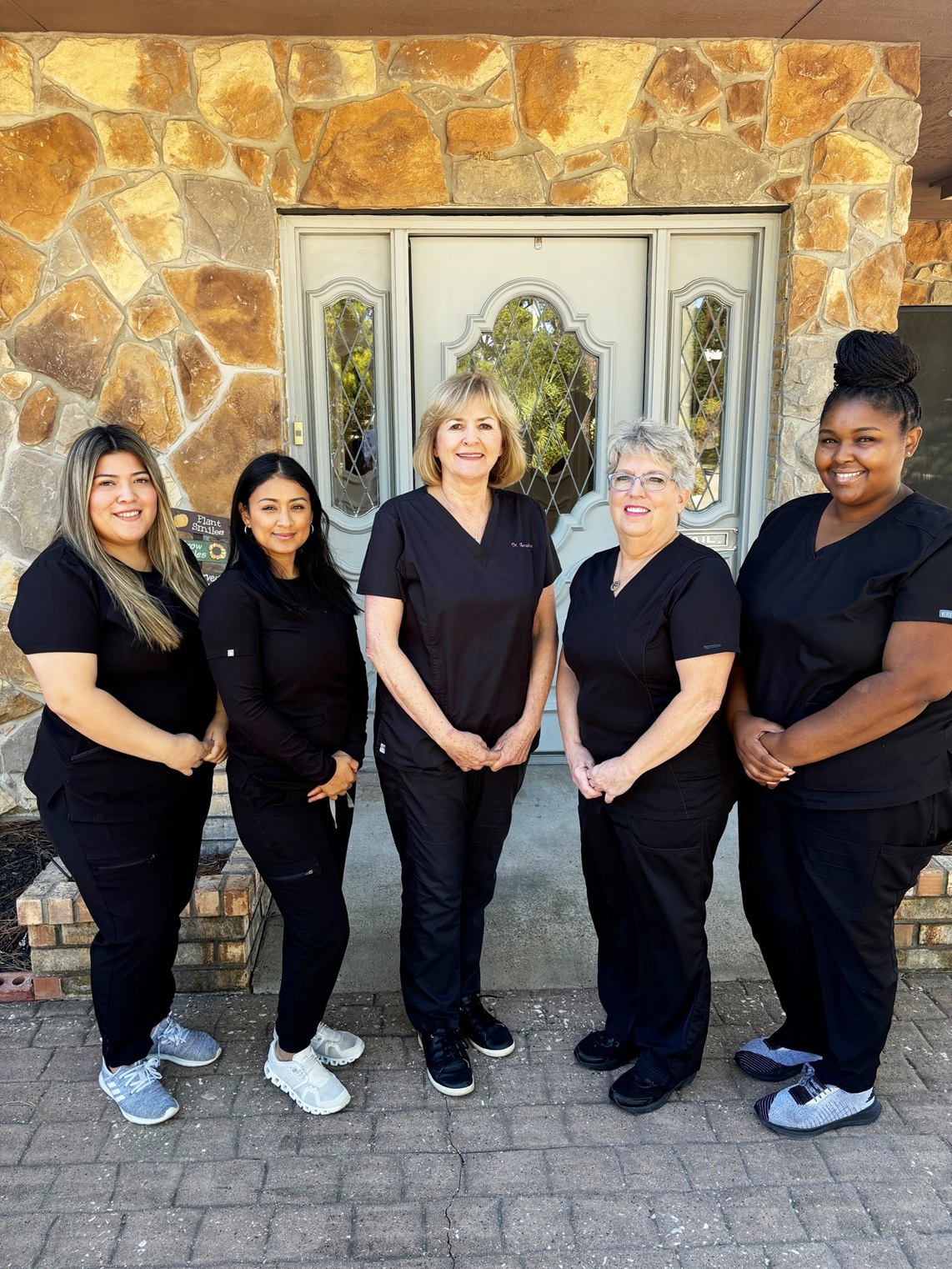
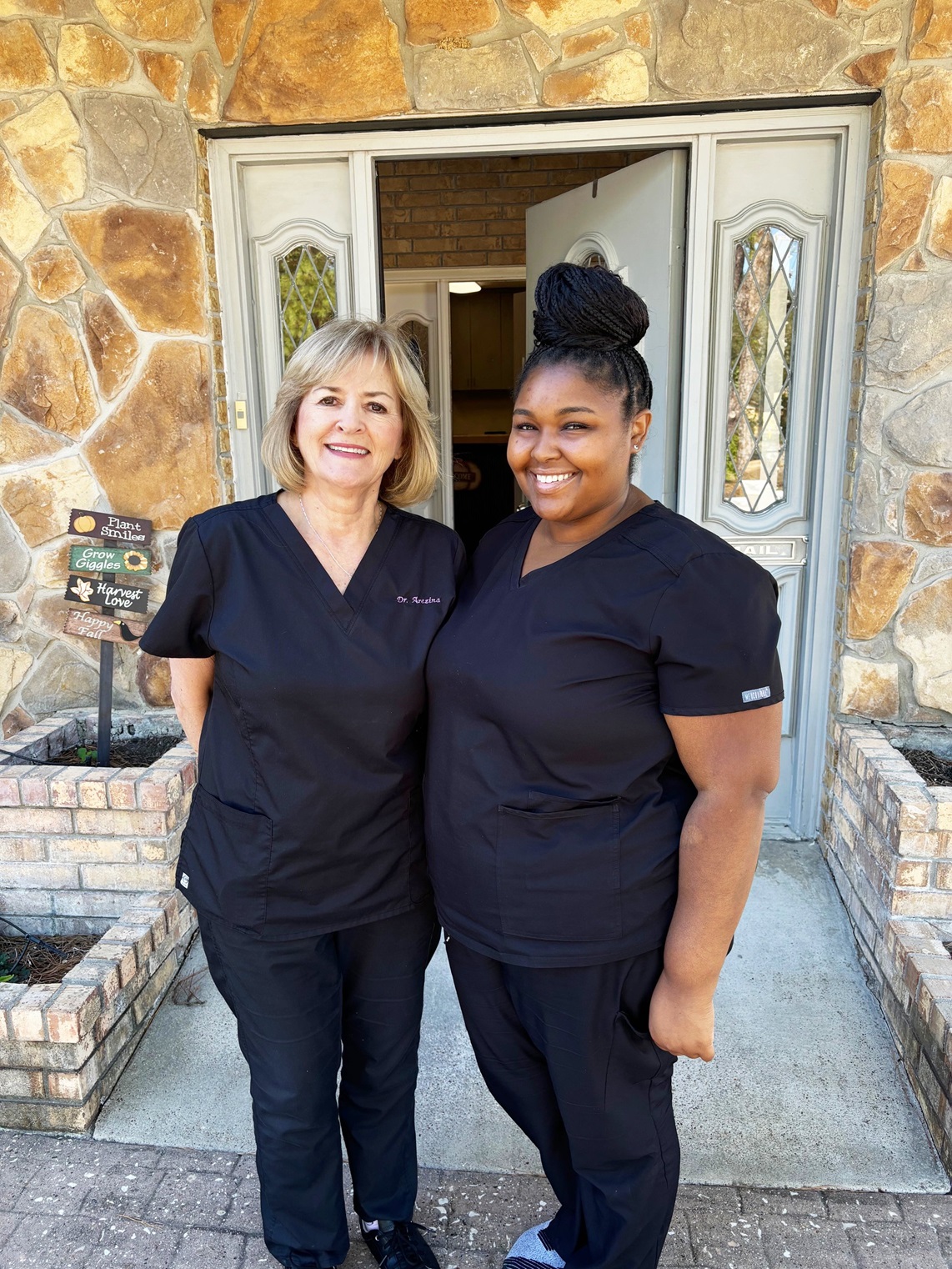
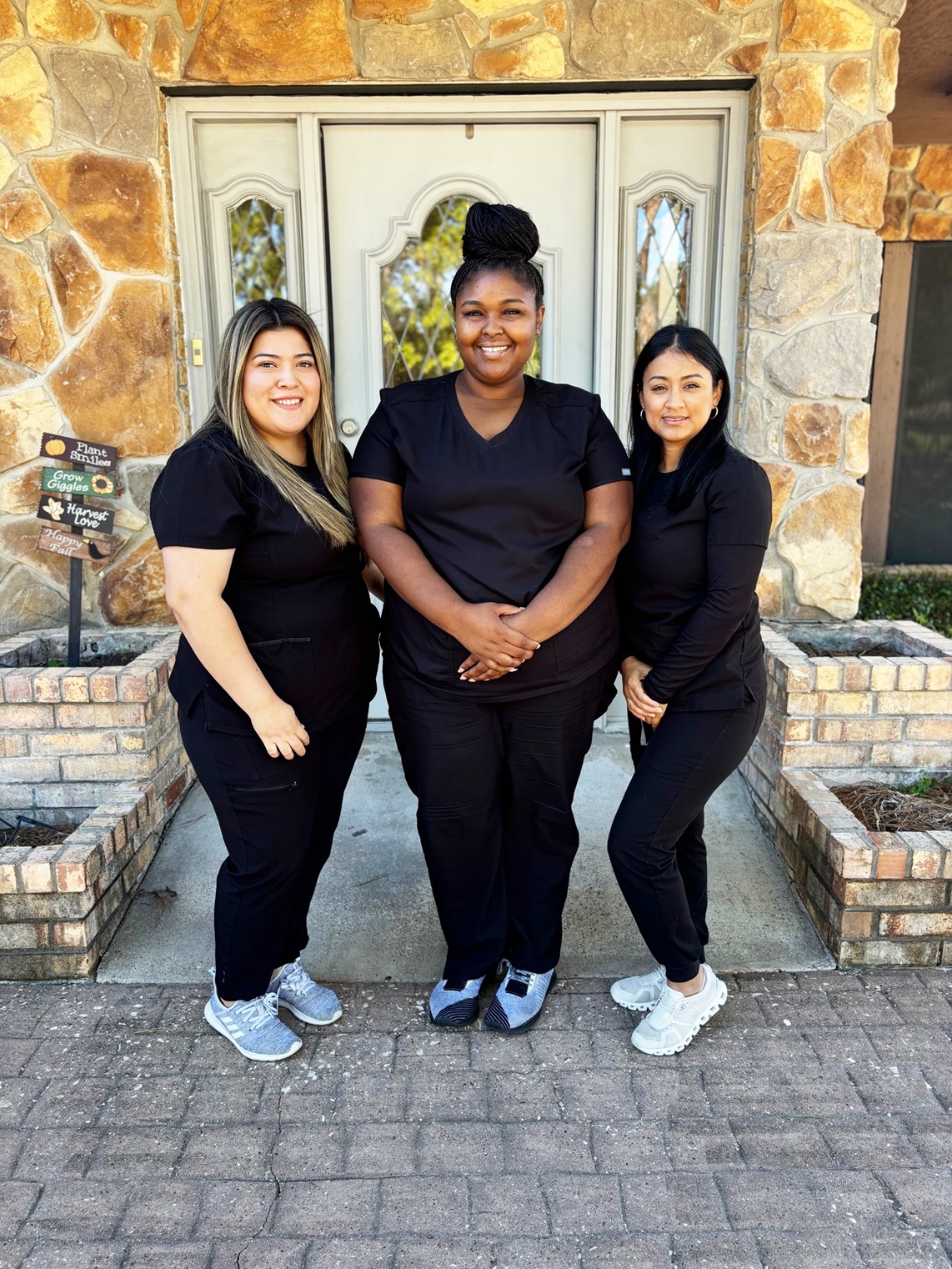
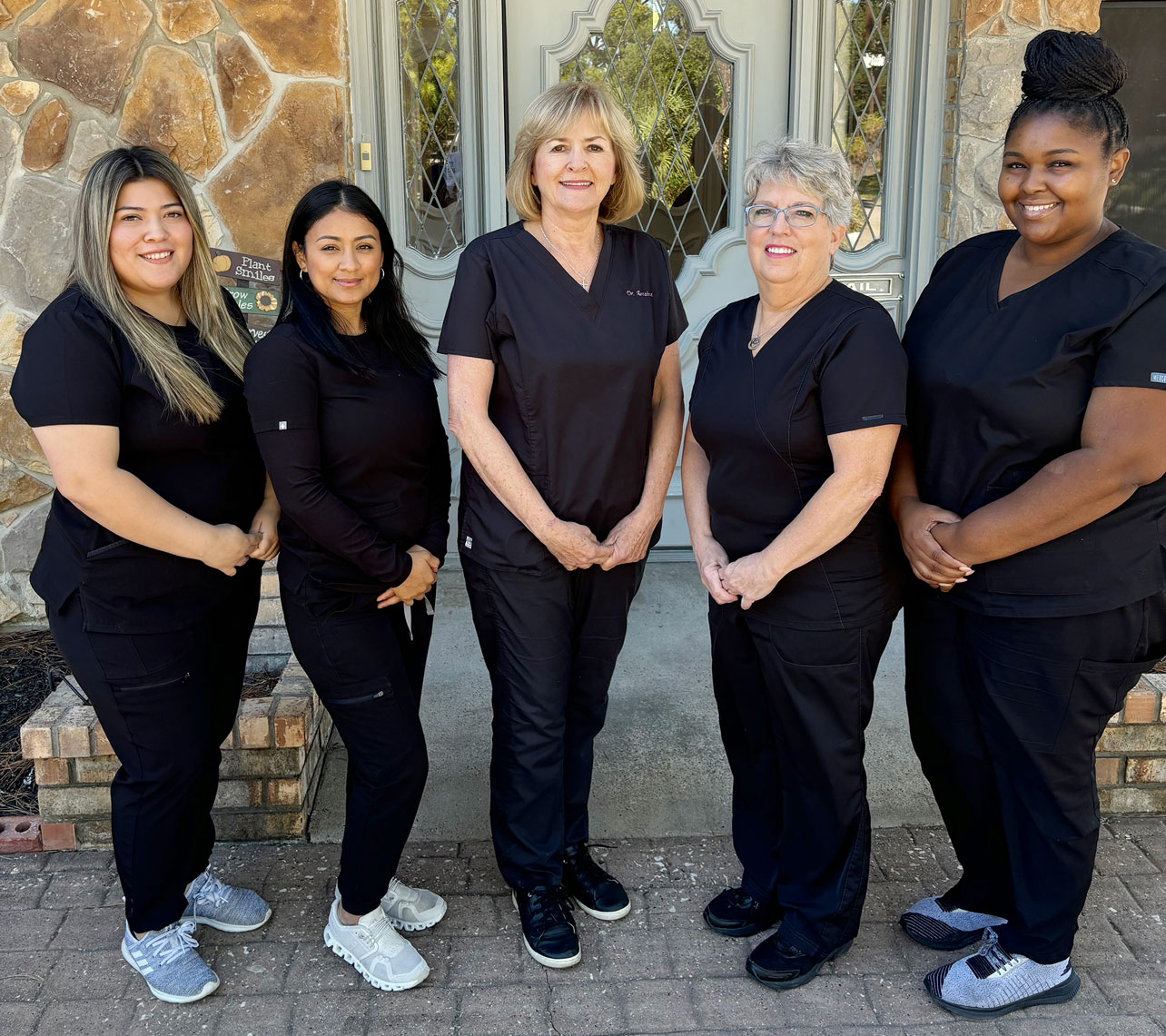
Meet The Team

Dr. Vesna Arezina
Dr. Arezina completed her undergraduate studies, majoring in Chemistry at The University of Houston and earned her Doctor of Dental Surgery degree from The University of Texas Dental Branch in the Texas Medical Center. Dr. Arezina has a passion for cosmetic and family dentistry, and regularly attends continuing education classes to learn about the state-of-the-art dental technology that she applies during patient treatments.
General Dentistry in Houston, TX
General dentistry encompasses an array of services and treatments with the common goal of preserving the natural teeth, maintaining oral health, and ensuring confidence in your smile.
Dr. Arezina and her staff located near you in Houston want to educate their patients, current and new, on the services and the procedures offered in the field of general dentistry.
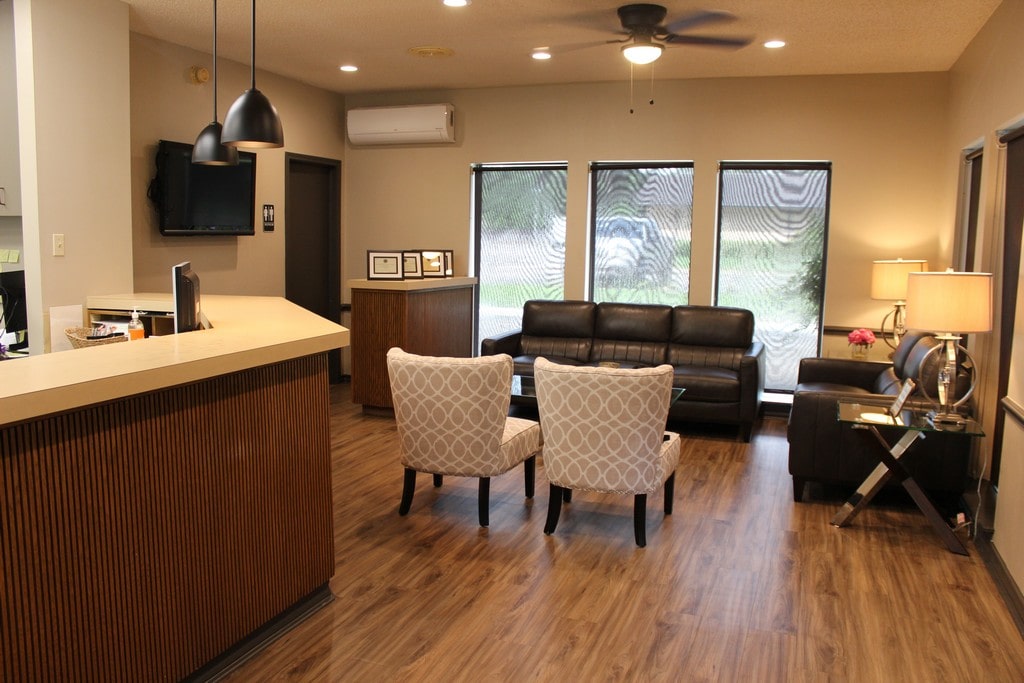
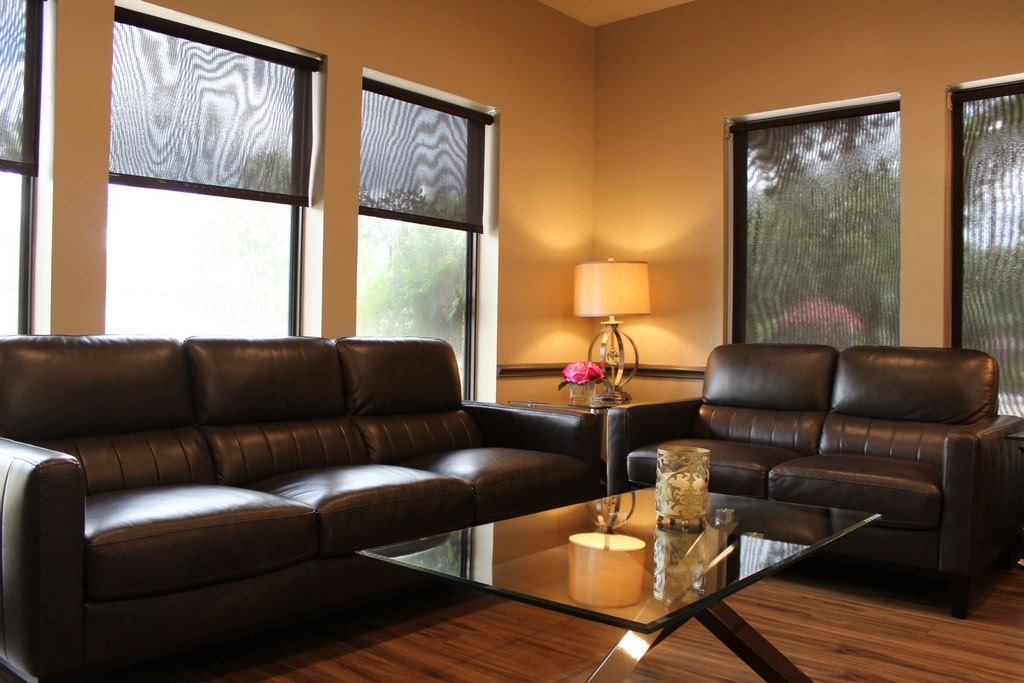
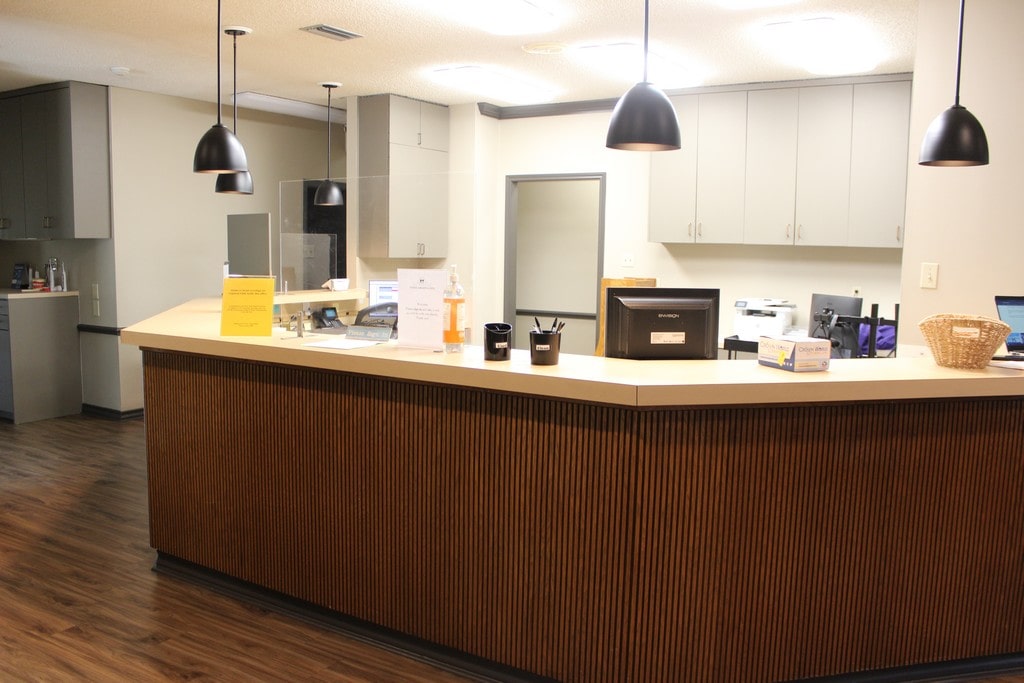
Office Tour
Visit Our Office
Office Hours
- Monday7:00 am - 5:00 pm
- Tuesday7:00 am - 6:00 pm
- WednesdayClosed
- Thursday7:00 am - 5:00 pm
- FridayClosed
- Saturday9:00 am - 2:00 pm
- SundayClosed
Northwest Villages Dentistry - Vesna Arezina DDS
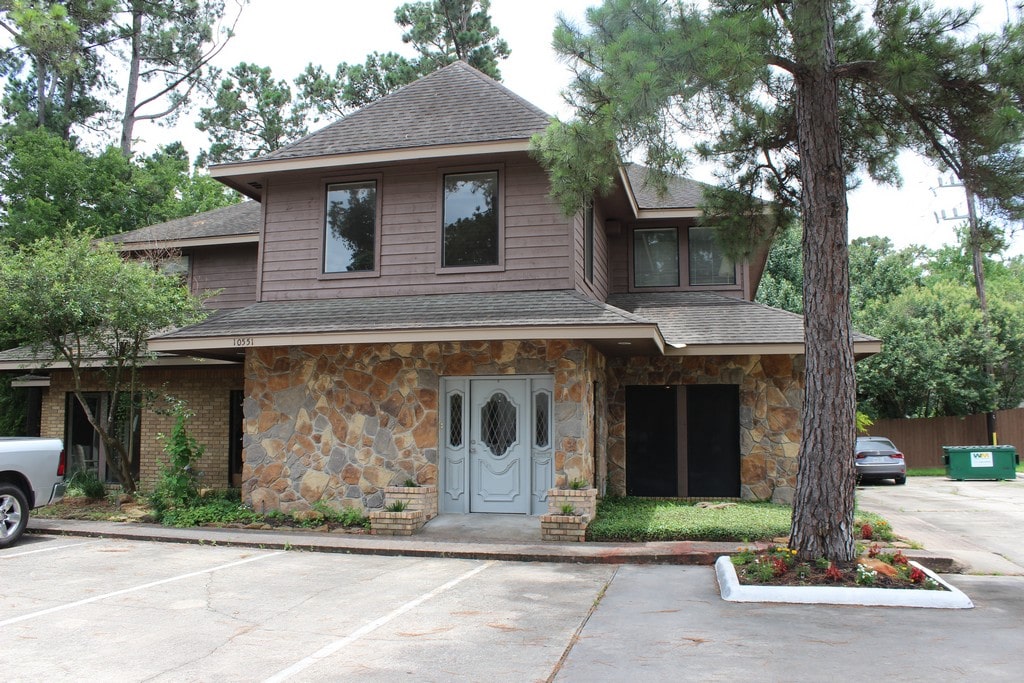
Location
10551 MILLS RD,
Houston, TX, 77070
Phone: (281) 469-7469Text Us: (281) 469-7469
Exciting News!
We're thrilled to offer Invisalign at our practice!
Ready to transform your smile? Schedule a consultation today and let Invisalign help you achieve the smile of your dreams.

Request an Appointment Call Now